Prevention and Detection

Prevention
Prevention demands detection of subclinical inflammatory patterns that must be addressed. Optimal health requires treatment of inflammation, lymph congestion, hormone imbalances, and dietary factors that eventually lead to organ dysfunction or ill-health.
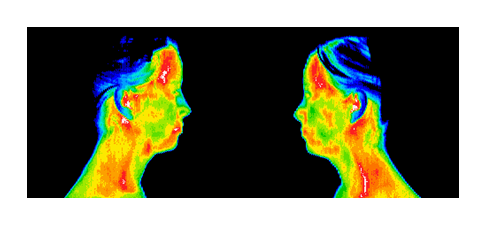
Elevated CRP h/s (C Reactive Protein) is an early risk indicator for heart disease. CRP gives us a gauge of the amount of inflammation in the body. When CRP is elevated AND the thermal image indicates high activity in the carotid region, there’s a VERY strong correlation to the early development of heart disease. When our interpreting physicians sees this type of thermal image, a CRP and carotid ultrasound is strongly advised.
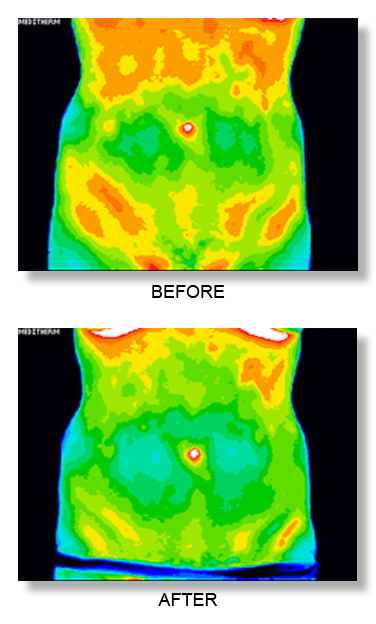
(09/2013) Before: ABDOMEN:Thermal activity throughout the upper abdomen has intensified compared to 9-19-2011 and is more extensive towards the right. Hepatic dysfunction is a consideration and laboratory assessment is recommended. Hyperthermia involving the lower pelvis R > L has increased and appears to be lymph related. No finding is evident with regards to the pelvic viscera
(09/2014) After: ABDOMEN:Upper quadrant thermal activity has decreased compared to 9-27-2013. Residual thermal activity is evident towards the left and may correspond to the spleen or to the splenic flexure region of the large bowel. No current finding is evident with regards to the liver. Pelvic level thermal activity has largely resolved as well. There is no indication as to current visceral dysfunction. Abdominal region thermal activity has likewise decreased and the recent change in diet may have relevance.
Detection
DITI provides the benefit of early detection of functional change but is NOT a stand alone technology and is not designed to replace current imaging modalities.
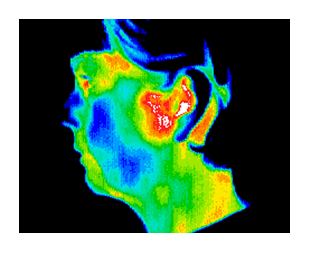
TMJ can be difficult to diagnose. This patient had classic symptoms and also classic thermographic findings consistent with TMJ which helps to confirm a diagnosis.
The majority of suspicious findings are benign but it is important to identify anything that needs further investigation or to be monitored more closely until there are findings that can be used in the decision making process. The hyperthermic findings in this breast did not cause concern in conjunction with the history and clinical information relating to symptoms. These findings were consistent with this patients mastitis.
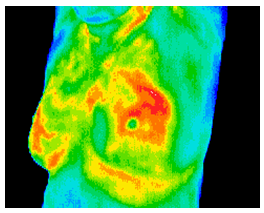
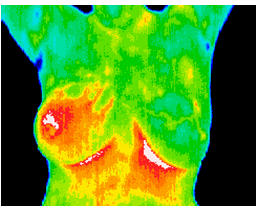
The results of this routine study led to the diagnosis of inflammatory carcinoma in the right breast. There were no clinical indications at this stage. (Thermography can show significant indicators several months before any of the clinical signs of inflammatory breast disease, skin discoloration, swelling and pain). Inflammatory breast disease cannot be detected by mammography and is most commonly seen in younger women, the prognosis is always poor. Early detection provides the best hope of survival.
